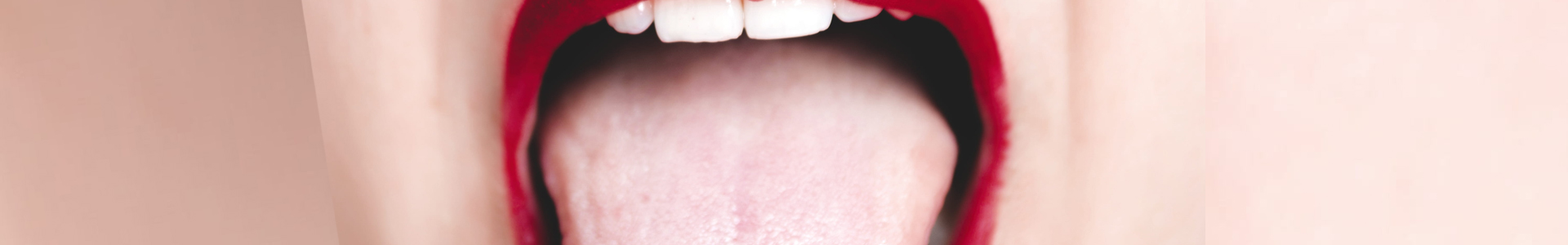
Sialolithiasis

What is Sialolithiasis
Sialolithiasis is a condition where a stone or mass forms inside a salivary gland, most commonly in the duct of the submandibular gland (Wharton's duct). Less frequently, stones may form in the duct of the parotid gland, and even more rarely in the sublingual glands or minor salivary glands.

What is Sialolithiasis
Sialolithiasis is a condition where a stone or mass forms inside a salivary gland, most commonly in the duct of the submandibular gland (Wharton's duct). Less frequently, stones may form in the duct of the parotid gland, and even more rarely in the sublingual glands or minor salivary glands.

What is Sialolithiasis
Sialolithiasis is a condition where a stone or mass forms inside a salivary gland, most commonly in the duct of the submandibular gland (Wharton's duct). Less frequently, stones may form in the duct of the parotid gland, and even more rarely in the sublingual glands or minor salivary glands.

Symptoms:
Common symptoms of sialolithiasis include:
- Pain and swelling in the affected salivary gland, which worsens especially when salivation is stimulated (e.g., by the sight, smell, or taste of food, hunger, or chewing gum). This is often referred to as "mealtime syndrome."
- Inflammation or infection of the gland can develop as a result.

Symptoms:
Common symptoms of sialolithiasis include:
- Pain and swelling in the affected salivary gland, which worsens especially when salivation is stimulated (e.g., by the sight, smell, or taste of food, hunger, or chewing gum). This is often referred to as "mealtime syndrome."
- Inflammation or infection of the gland can develop as a result.

Symptoms:
Common symptoms of sialolithiasis include:
- Pain and swelling in the affected salivary gland, which worsens especially when salivation is stimulated (e.g., by the sight, smell, or taste of food, hunger, or chewing gum). This is often referred to as "mealtime syndrome."
- Inflammation or infection of the gland can develop as a result.

Causes:
Sialolithiasis may be caused by various factors, such as:
- Infection of the salivary glands
- Dehydration (e.g., due to medications like phenothiazines)
- Autoimmune diseases like Sjögren's syndrome
- Elevated calcium levels (e.g., hyperparathyroidism)
- In many cases, the cause is idiopathic (unknown).

Causes:
Sialolithiasis may be caused by various factors, such as:
- Infection of the salivary glands
- Dehydration (e.g., due to medications like phenothiazines)
- Autoimmune diseases like Sjögren's syndrome
- Elevated calcium levels (e.g., hyperparathyroidism)
- In many cases, the cause is idiopathic (unknown).

Causes:
Sialolithiasis may be caused by various factors, such as:
- Infection of the salivary glands
- Dehydration (e.g., due to medications like phenothiazines)
- Autoimmune diseases like Sjögren's syndrome
- Elevated calcium levels (e.g., hyperparathyroidism)
- In many cases, the cause is idiopathic (unknown).
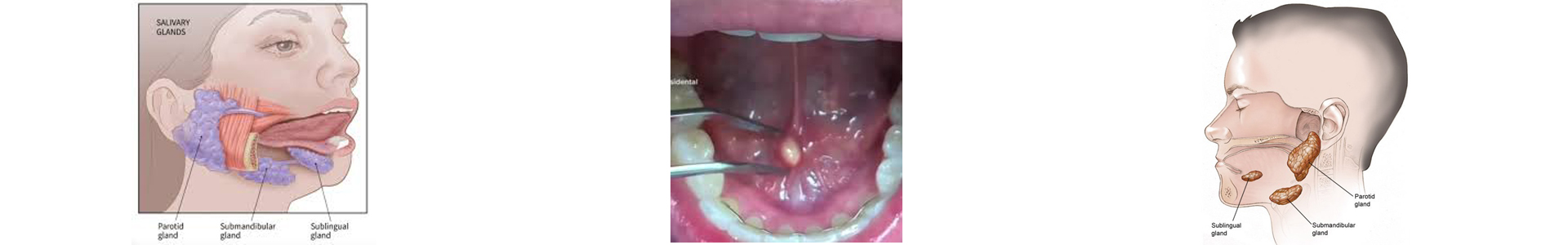

Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis of sialolithiasis is made through clinical examination and imaging methods like ultrasound or sialography. Treatment typically involves:
- Conservative measures such as increasing fluid intake and applying warm compresses.
- In more severe or recurrent cases, surgical removal of the stone or the affected gland may be necessary.

Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis of sialolithiasis is made through clinical examination and imaging methods like ultrasound or sialography. Treatment typically involves:
- Conservative measures such as increasing fluid intake and applying warm compresses.
- In more severe or recurrent cases, surgical removal of the stone or the affected gland may be necessary.

Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis of sialolithiasis is made through clinical examination and imaging methods like ultrasound or sialography. Treatment typically involves:
- Conservative measures such as increasing fluid intake and applying warm compresses.
- In more severe or recurrent cases, surgical removal of the stone or the affected gland may be necessary.

Frequency:
Common symptoms of sialolithiasis include:
- Pain and swelling in the affected salivary gland, which worsens especially when salivation is stimulated (e.g., by the sight, smell, or taste of food, hunger, or chewing gum). This is often referred to as "mealtime syndrome."
- Inflammation or infection of the gland can develop as a result.

Frequency:
Common symptoms of sialolithiasis include:
- Pain and swelling in the affected salivary gland, which worsens especially when salivation is stimulated (e.g., by the sight, smell, or taste of food, hunger, or chewing gum). This is often referred to as "mealtime syndrome."
- Inflammation or infection of the gland can develop as a result.

Frequency:
Common symptoms of sialolithiasis include:
- Pain and swelling in the affected salivary gland, which worsens especially when salivation is stimulated (e.g., by the sight, smell, or taste of food, hunger, or chewing gum). This is often referred to as "mealtime syndrome."
- Inflammation or infection of the gland can develop as a result.

Prevention:
Preventative measures for sialolithiasis include maintaining good oral hygiene, staying well-hydrated, and regular monitoring, especially for those at higher risk. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent complications such as infections and chronic inflammation of the salivary glands.

Prevention:
Preventative measures for sialolithiasis include maintaining good oral hygiene, staying well-hydrated, and regular monitoring, especially for those at higher risk. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent complications such as infections and chronic inflammation of the salivary glands.

Prevention:
Preventative measures for sialolithiasis include maintaining good oral hygiene, staying well-hydrated, and regular monitoring, especially for those at higher risk. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent complications such as infections and chronic inflammation of the salivary glands.