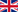
Facial Bone Fractures

What are facial fractures?
Facial fractures are injuries that cause breaks or cracks in the bones of the face and affect important functions such as breathing, chewing, and speaking. Our face is made up of many bones that work together to allow us to express ourselves and communicate. An injury to these bones requires immediate diagnosis and appropriate treatment to fully restore both the function and appearance of the face.

What are facial fractures?
Facial fractures are injuries that cause breaks or cracks in the bones of the face and affect important functions such as breathing, chewing, and speaking. Our face is made up of many bones that work together to allow us to express ourselves and communicate. An injury to these bones requires immediate diagnosis and appropriate treatment to fully restore both the function and appearance of the face.

What are facial fractures?
Facial fractures are injuries that cause breaks or cracks in the bones of the face and affect important functions such as breathing, chewing, and speaking. Our face is made up of many bones that work together to allow us to express ourselves and communicate. An injury to these bones requires immediate diagnosis and appropriate treatment to fully restore both the function and appearance of the face.

What are facial fractures?
The most common types of facial fractures include:
Mandibular Fractures
The lower jaw may break due to a blow, fall, or car accident. These fractures cause pain, difficulty opening the mouth, and changes in the alignment of the teeth.Maxillary Fractures
The upper jaw supports the middle part of the face and the lower parts of the eyes. Fractures in the upper jaw may affect breathing, chewing, and vision.Zygomatic Bone Fractures
The zygomatic bone forms the "cheekbone" of the face. When this bone breaks, there is noticeable sagging or asymmetry of the face, pain around the eye, and problems with jaw movement.Nasal Fractures
Nasal fractures are among the most common and cause bleeding, swelling, and sometimes difficulty breathing.Orbital Fractures
Injury to the bone surrounding the eye can cause diplopia (double vision), swelling, and misalignment of the eye.

What are facial fractures?
The most common types of facial fractures include:
Mandibular Fractures
The lower jaw may break due to a blow, fall, or car accident. These fractures cause pain, difficulty opening the mouth, and changes in the alignment of the teeth.Maxillary Fractures
The upper jaw supports the middle part of the face and the lower parts of the eyes. Fractures in the upper jaw may affect breathing, chewing, and vision.Zygomatic Bone Fractures
The zygomatic bone forms the "cheekbone" of the face. When this bone breaks, there is noticeable sagging or asymmetry of the face, pain around the eye, and problems with jaw movement.Nasal Fractures
Nasal fractures are among the most common and cause bleeding, swelling, and sometimes difficulty breathing.Orbital Fractures
Injury to the bone surrounding the eye can cause diplopia (double vision), swelling, and misalignment of the eye.

What are facial fractures?
The most common types of facial fractures include:
Mandibular Fractures
The lower jaw may break due to a blow, fall, or car accident. These fractures cause pain, difficulty opening the mouth, and changes in the alignment of the teeth.Maxillary Fractures
The upper jaw supports the middle part of the face and the lower parts of the eyes. Fractures in the upper jaw may affect breathing, chewing, and vision.Zygomatic Bone Fractures
The zygomatic bone forms the "cheekbone" of the face. When this bone breaks, there is noticeable sagging or asymmetry of the face, pain around the eye, and problems with jaw movement.Nasal Fractures
Nasal fractures are among the most common and cause bleeding, swelling, and sometimes difficulty breathing.Orbital Fractures
Injury to the bone surrounding the eye can cause diplopia (double vision), swelling, and misalignment of the eye.

Causes of Facial Fractures
Facial fractures are primarily caused by car accidents, sports injuries, falls, or physical assaults. Any significant impact to the face can lead to a fracture, especially if there is a predisposition due to bone sensitivity, such as in individuals with osteoporosis.

Causes of Facial Fractures
Facial fractures are primarily caused by car accidents, sports injuries, falls, or physical assaults. Any significant impact to the face can lead to a fracture, especially if there is a predisposition due to bone sensitivity, such as in individuals with osteoporosis.

Causes of Facial Fractures
Facial fractures are primarily caused by car accidents, sports injuries, falls, or physical assaults. Any significant impact to the face can lead to a fracture, especially if there is a predisposition due to bone sensitivity, such as in individuals with osteoporosis.

Symptoms of Facial Fractures
The symptoms of a facial fracture vary depending on the type and severity of the injury, but they usually include:
Pain and tenderness at the site of the injury
Swelling and bruising around the face and eyes
Difficulty opening the mouth or chewing
Bleeding from the nose or mouth
Change in facial symmetry or deformity
Numbness in areas of the face
Diplopia (double vision), if the orbital bone is fractured

Symptoms of Facial Fractures
The symptoms of a facial fracture vary depending on the type and severity of the injury, but they usually include:
Pain and tenderness at the site of the injury
Swelling and bruising around the face and eyes
Difficulty opening the mouth or chewing
Bleeding from the nose or mouth
Change in facial symmetry or deformity
Numbness in areas of the face
Diplopia (double vision), if the orbital bone is fractured

Symptoms of Facial Fractures
The symptoms of a facial fracture vary depending on the type and severity of the injury, but they usually include:
Pain and tenderness at the site of the injury
Swelling and bruising around the face and eyes
Difficulty opening the mouth or chewing
Bleeding from the nose or mouth
Change in facial symmetry or deformity
Numbness in areas of the face
Diplopia (double vision), if the orbital bone is fractured
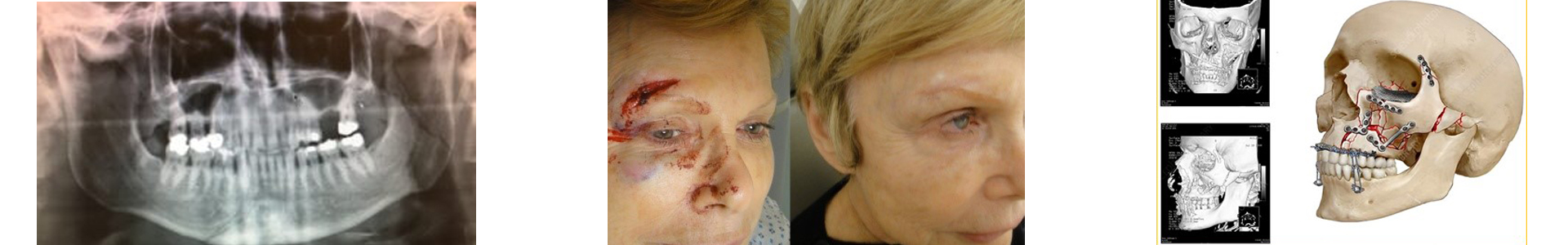

How are Facial Fractures Diagnosed?
The diagnosis is made through a clinical examination by a specialized oral and maxillofacial surgeon, who will observe the characteristic symptoms and conduct imaging tests. Usually, the doctor will recommend X-rays or a CT scan to determine the exact location and severity of the fracture. Imaging tests are essential for accurate assessment and selecting the most appropriate treatment.

How are Facial Fractures Diagnosed?
The diagnosis is made through a clinical examination by a specialized oral and maxillofacial surgeon, who will observe the characteristic symptoms and conduct imaging tests. Usually, the doctor will recommend X-rays or a CT scan to determine the exact location and severity of the fracture. Imaging tests are essential for accurate assessment and selecting the most appropriate treatment.

How are Facial Fractures Diagnosed?
The diagnosis is made through a clinical examination by a specialized oral and maxillofacial surgeon, who will observe the characteristic symptoms and conduct imaging tests. Usually, the doctor will recommend X-rays or a CT scan to determine the exact location and severity of the fracture. Imaging tests are essential for accurate assessment and selecting the most appropriate treatment.

Management of Facial Fractures
The treatment depends on the type and extent of the fracture. In mild fractures, the treatment may include rest, cold compresses, and avoiding pressure on the injured area. In more severe cases, surgery is necessary to restore the proper position of the bones, using titanium plates and screws.
Recovery may take from a few weeks to months, depending on the severity of the fracture and the patient's age.

Management of Facial Fractures
The treatment depends on the type and extent of the fracture. In mild fractures, the treatment may include rest, cold compresses, and avoiding pressure on the injured area. In more severe cases, surgery is necessary to restore the proper position of the bones, using titanium plates and screws.
Recovery may take from a few weeks to months, depending on the severity of the fracture and the patient's age.

Management of Facial Fractures
The treatment depends on the type and extent of the fracture. In mild fractures, the treatment may include rest, cold compresses, and avoiding pressure on the injured area. In more severe cases, surgery is necessary to restore the proper position of the bones, using titanium plates and screws.
Recovery may take from a few weeks to months, depending on the severity of the fracture and the patient's age.

Complications of Facial Fractures
If a facial fracture is not properly treated, serious complications may arise, such as:
- Persistent pain or deformity
- Dysfunction in the alignment of the teeth
- Loss of sensation or numbness in areas of the face
- Diplopia (double vision) or other vision disturbances
- Infections in the fractured bone or soft tissues of the face
Early diagnosis and treatment minimize the risk of these complications.

Complications of Facial Fractures
If a facial fracture is not properly treated, serious complications may arise, such as:
- Persistent pain or deformity
- Dysfunction in the alignment of the teeth
- Loss of sensation or numbness in areas of the face
- Diplopia (double vision) or other vision disturbances
- Infections in the fractured bone or soft tissues of the face
Early diagnosis and treatment minimize the risk of these complications.

Complications of Facial Fractures
If a facial fracture is not properly treated, serious complications may arise, such as:
- Persistent pain or deformity
- Dysfunction in the alignment of the teeth
- Loss of sensation or numbness in areas of the face
- Diplopia (double vision) or other vision disturbances
- Infections in the fractured bone or soft tissues of the face
Early diagnosis and treatment minimize the risk of these complications.

How Can Facial Fractures Be Prevented?
Prevention of facial fractures is very important. The use of seat belts while driving, helmets for motorcycles and bicycles, as well as protective gear during sports such as football and rugby, can reduce the risk of serious injuries. Additionally, preventing falls in the elderly and proper treatment of osteoporosis are crucial.

How Can Facial Fractures Be Prevented?
Prevention of facial fractures is very important. The use of seat belts while driving, helmets for motorcycles and bicycles, as well as protective gear during sports such as football and rugby, can reduce the risk of serious injuries. Additionally, preventing falls in the elderly and proper treatment of osteoporosis are crucial.

How Can Facial Fractures Be Prevented?
Prevention of facial fractures is very important. The use of seat belts while driving, helmets for motorcycles and bicycles, as well as protective gear during sports such as football and rugby, can reduce the risk of serious injuries. Additionally, preventing falls in the elderly and proper treatment of osteoporosis are crucial.

Conclusion
Facial fractures are serious injuries that require immediate diagnosis and treatment by a specialized physician. If not properly managed, they can cause permanent complications. However, with the right treatment and appropriate care, patients can fully recover and restore the aesthetics and functionality of their face.

Conclusion
Facial fractures are serious injuries that require immediate diagnosis and treatment by a specialized physician. If not properly managed, they can cause permanent complications. However, with the right treatment and appropriate care, patients can fully recover and restore the aesthetics and functionality of their face.

Conclusion
Facial fractures are serious injuries that require immediate diagnosis and treatment by a specialized physician. If not properly managed, they can cause permanent complications. However, with the right treatment and appropriate care, patients can fully recover and restore the aesthetics and functionality of their face.