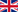
Precancerous Lesions of the Mouth

Precancerous Lesions of the Mouth
Precancerous lesions of the mouth are alterations of the oral tissues that carry an increased risk of developing into squamous cell carcinoma, the most common type of oral cancer. Although not all lesions progress to cancer, early identification and management are critical for preventing serious conditions.

Precancerous Lesions of the Mouth
Precancerous lesions of the mouth are alterations of the oral tissues that carry an increased risk of developing into squamous cell carcinoma, the most common type of oral cancer. Although not all lesions progress to cancer, early identification and management are critical for preventing serious conditions.

Precancerous Lesions of the Mouth
Precancerous lesions of the mouth are alterations of the oral tissues that carry an increased risk of developing into squamous cell carcinoma, the most common type of oral cancer. Although not all lesions progress to cancer, early identification and management are critical for preventing serious conditions.

What are the main precancerous lesions?
- Leukoplakia: White patches in the mouth that cannot be scraped off and cannot be attributed to any other diagnosis. It is the most common precancerous lesion.
- Erythroplakia: Red lesions with a higher rate of malignant transformation than leukoplakia.
- Oral lichen planus (especially the erythroleukoplastic form): A chronic inflammatory condition with potential epithelial dysplasia.
- Actinic cheilitis: A lesion of the lower lip caused by chronic sun exposure, with a predisposition to malignancy.
- Hyperplastic or dysplastic lesions: Areas of excessive cell growth or dysplasia that may progress to cancer.

What are the main precancerous lesions?
- Leukoplakia: White patches in the mouth that cannot be scraped off and cannot be attributed to any other diagnosis. It is the most common precancerous lesion.
- Erythroplakia: Red lesions with a higher rate of malignant transformation than leukoplakia.
- Oral lichen planus (especially the erythroleukoplastic form): A chronic inflammatory condition with potential epithelial dysplasia.
- Actinic cheilitis: A lesion of the lower lip caused by chronic sun exposure, with a predisposition to malignancy.
- Hyperplastic or dysplastic lesions: Areas of excessive cell growth or dysplasia that may progress to cancer.

What are the main precancerous lesions?
- Leukoplakia: White patches in the mouth that cannot be scraped off and cannot be attributed to any other diagnosis. It is the most common precancerous lesion.
- Erythroplakia: Red lesions with a higher rate of malignant transformation than leukoplakia.
- Oral lichen planus (especially the erythroleukoplastic form): A chronic inflammatory condition with potential epithelial dysplasia.
- Actinic cheilitis: A lesion of the lower lip caused by chronic sun exposure, with a predisposition to malignancy.
- Hyperplastic or dysplastic lesions: Areas of excessive cell growth or dysplasia that may progress to cancer.

What are the risk factors?
- Smoking and use of tobacco products (including chewing tobacco)
- Alcohol consumption, especially in combination with smoking
- Chronic mechanical irritation (poor prosthetic restorations, injuries)
- HPV infection (particularly type 16)
- Poor oral hygiene
- Excessive sun exposure (for the lower lip)

What are the risk factors?
- Smoking and use of tobacco products (including chewing tobacco)
- Alcohol consumption, especially in combination with smoking
- Chronic mechanical irritation (poor prosthetic restorations, injuries)
- HPV infection (particularly type 16)
- Poor oral hygiene
- Excessive sun exposure (for the lower lip)

What are the risk factors?
- Smoking and use of tobacco products (including chewing tobacco)
- Alcohol consumption, especially in combination with smoking
- Chronic mechanical irritation (poor prosthetic restorations, injuries)
- HPV infection (particularly type 16)
- Poor oral hygiene
- Excessive sun exposure (for the lower lip)

What are the symptoms?
Precancerous lesions may appear as:
- White or red plaques or spots
- Thickening or hardening of the oral tissue
- Small sores or ulcers that do not heal
- Irritation, pain, or difficulty chewing and swallowing
In many cases, the lesions are asymptomatic, which is why preventive screening is necessary.

What are the symptoms?
Precancerous lesions may appear as:
- White or red plaques or spots
- Thickening or hardening of the oral tissue
- Small sores or ulcers that do not heal
- Irritation, pain, or difficulty chewing and swallowing
In many cases, the lesions are asymptomatic, which is why preventive screening is necessary.

What are the symptoms?
Precancerous lesions may appear as:
- White or red plaques or spots
- Thickening or hardening of the oral tissue
- Small sores or ulcers that do not heal
- Irritation, pain, or difficulty chewing and swallowing
In many cases, the lesions are asymptomatic, which is why preventive screening is necessary.
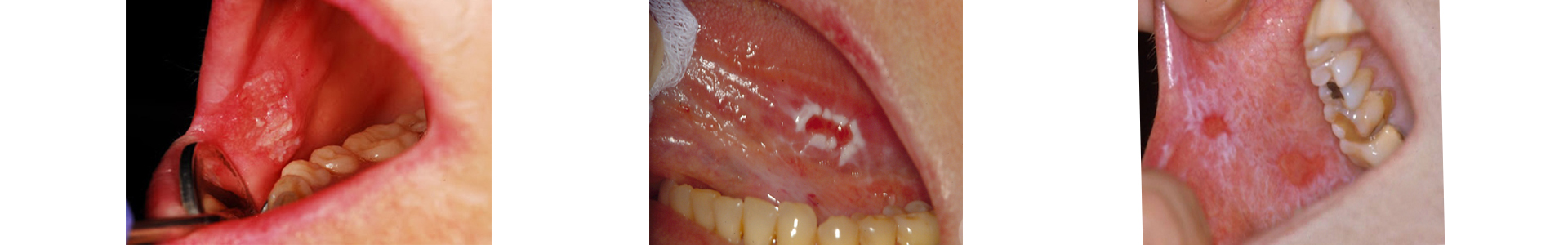

How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis includes:
- Clinical examination by a specialized doctor
- Biopsy of the suspicious lesion for histological evaluation and determination of potential dysplasia
- In some cases, the use of supplementary methods such as tomography or staining
Biopsy is the only definitive method for diagnosing precancerous lesions.

How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis includes:
- Clinical examination by a specialized doctor
- Biopsy of the suspicious lesion for histological evaluation and determination of potential dysplasia
- In some cases, the use of supplementary methods such as tomography or staining
Biopsy is the only definitive method for diagnosing precancerous lesions.

How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis includes:
- Clinical examination by a specialized doctor
- Biopsy of the suspicious lesion for histological evaluation and determination of potential dysplasia
- In some cases, the use of supplementary methods such as tomography or staining
Biopsy is the only definitive method for diagnosing precancerous lesions.

What is the treatment?
The treatment depends on the type and severity of the lesion:
- Monitoring: For mild lesions without dysplasia, with regular follow-up checks.
- Surgical excision: For dysplastic lesions or high-risk lesions.
- Management of risk factors: Cessation of smoking and alcohol use, improvement of oral hygiene, correction of traumatic causes.
Early intervention can prevent the development of cancer.

What is the treatment?
The treatment depends on the type and severity of the lesion:
- Monitoring: For mild lesions without dysplasia, with regular follow-up checks.
- Surgical excision: For dysplastic lesions or high-risk lesions.
- Management of risk factors: Cessation of smoking and alcohol use, improvement of oral hygiene, correction of traumatic causes.
Early intervention can prevent the development of cancer.

What is the treatment?
The treatment depends on the type and severity of the lesion:
- Monitoring: For mild lesions without dysplasia, with regular follow-up checks.
- Surgical excision: For dysplastic lesions or high-risk lesions.
- Management of risk factors: Cessation of smoking and alcohol use, improvement of oral hygiene, correction of traumatic causes.
Early intervention can prevent the development of cancer.

Prevention
Prevention is based on reducing risk factors and early detection:
- Cessation of smoking and limitation of alcohol consumption
- Daily oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups
- Use of sunscreen on the lips for individuals with increased sun exposure
- Immediate examination of any oral lesion that persists for more than two weeks

Prevention
Prevention is based on reducing risk factors and early detection:
- Cessation of smoking and limitation of alcohol consumption
- Daily oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups
- Use of sunscreen on the lips for individuals with increased sun exposure
- Immediate examination of any oral lesion that persists for more than two weeks

Prevention
Prevention is based on reducing risk factors and early detection:
- Cessation of smoking and limitation of alcohol consumption
- Daily oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups
- Use of sunscreen on the lips for individuals with increased sun exposure
- Immediate examination of any oral lesion that persists for more than two weeks

Conclusion
Precancerous lesions of the mouth are a serious but manageable condition if diagnosed and treated early. Prevention, regular monitoring, and proper therapeutic approach are key to maintaining oral and overall health.

Conclusion
Precancerous lesions of the mouth are a serious but manageable condition if diagnosed and treated early. Prevention, regular monitoring, and proper therapeutic approach are key to maintaining oral and overall health.

Conclusion
Precancerous lesions of the mouth are a serious but manageable condition if diagnosed and treated early. Prevention, regular monitoring, and proper therapeutic approach are key to maintaining oral and overall health.