Frenectomy

What is the frenulum?
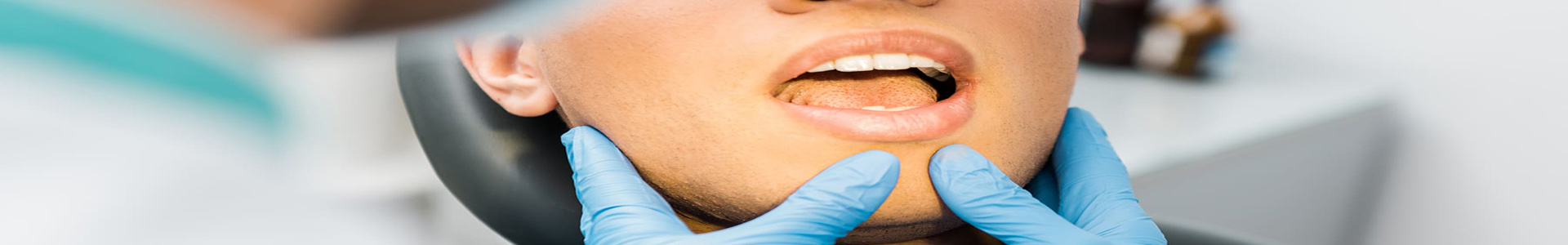
The frenulum is a normal anatomical structure found in the mouth. The problem arises when the frenulum is shorter than usual, as this can create a predisposition to periodontal disease, making it necessary to treat it immediately and effectively. Short frenulums are a common phenomenon and are mainly observed from pre-adolescence.
When the frenulum is short, it can affect mouth movements, speech and articulation. There are three types of frenulum: the lingual frenulum (at the base of the tongue), the upper lip frenulum and the lower lip frenulum. In some cases, the frenulum is quite strong and causes problems. For example:
- In the upper jaw, the frenulum can be located between the central sectors of the teeth and create a gap between them.
- In the lower jaw, it can pull the gums downward, causing recession or making it difficult to fit dentures.
- The lingual frenulum, when short, can cause a delay in the onset of speech and general speech problems.

What is the frenulum?
The frenulum is a normal anatomical structure found in the mouth. The problem arises when the frenulum is shorter than usual, as this can create a predisposition to periodontal disease, making it necessary to treat it immediately and effectively. Short frenulums are a common phenomenon and are mainly observed from pre-adolescence.
When the frenulum is short, it can affect mouth movements, speech and articulation. There are three types of frenulum: the lingual frenulum (at the base of the tongue), the upper lip frenulum and the lower lip frenulum. In some cases, the frenulum is quite strong and causes problems. For example:
- In the upper jaw, the frenulum can be located between the central sectors of the teeth and create a gap between them.
- In the lower jaw, it can pull the gums downward, causing recession or making it difficult to fit dentures.
- The lingual frenulum, when short, can cause a delay in the onset of speech and general speech problems.

What is the frenulum?
The frenulum is a normal anatomical structure found in the mouth. The problem arises when the frenulum is shorter than usual, as this can create a predisposition to periodontal disease, making it necessary to treat it immediately and effectively. Short frenulums are a common phenomenon and are mainly observed from pre-adolescence.
When the frenulum is short, it can affect mouth movements, speech and articulation. There are three types of frenulum: the lingual frenulum (at the base of the tongue), the upper lip frenulum and the lower lip frenulum. In some cases, the frenulum is quite strong and causes problems. For example:
- In the upper jaw, the frenulum can be located between the central sectors of the teeth and create a gap between them.
- In the lower jaw, it can pull the gums downward, causing recession or making it difficult to fit dentures.
- The lingual frenulum, when short, can cause a delay in the onset of speech and general speech problems.

When is a Chalinectomist performed?
Bridging is indicated in cases:
- When the short frenulum affects the smooth functioning of the mouth.
- When the frenulum prevents the placement of a denture.
- For aesthetic reasons.

When is a Chalinectomist performed?
Bridging is indicated in cases:
- When the short frenulum affects the smooth functioning of the mouth.
- When the frenulum prevents the placement of a denture.
- For aesthetic reasons.

When is a Chalinectomist performed?
Bridging is indicated in cases:
- When the short frenulum affects the smooth functioning of the mouth.
- When the frenulum prevents the placement of a denture.
- For aesthetic reasons.

How is Chalinectomectomy performed?
Treatment of short frenula is done either with Diode Laser or through Surgical intervention. The choice of method depends on the clinical appearance of the frenulum and the category it belongs to.
- Diode Laser: This is a very quick procedure, lasting 2-3 minutes, performed under local anesthesia. It is almost bloodless, with no need for stitches. There is no pain after the procedure, and healing takes place within a few days without leaving scars.
- Surgical Procedure: Performed under local anesthesia at the of the medical office. Healing is completed in a few days without scarring. The frenulum excision is painless and usually lasts only 10 minutes.

How is Chalinectomectomy performed?
Treatment of short frenula is done either with Diode Laser or through Surgical intervention. The choice of method depends on the clinical appearance of the frenulum and the category it belongs to.
- Diode Laser: This is a very quick procedure, lasting 2-3 minutes, performed under local anesthesia. It is almost bloodless, with no need for stitches. There is no pain after the procedure, and healing takes place within a few days without leaving scars.
- Surgical Procedure: Performed under local anesthesia at the of the medical office. Healing is completed in a few days without scarring. The frenulum excision is painless and usually lasts only 10 minutes.

How is Chalinectomectomy performed?
Treatment of short frenula is done either with Diode Laser or through Surgical intervention. The choice of method depends on the clinical appearance of the frenulum and the category it belongs to.
- Diode Laser: This is a very quick procedure, lasting 2-3 minutes, performed under local anesthesia. It is almost bloodless, with no need for stitches. There is no pain after the procedure, and healing takes place within a few days without leaving scars.
- Surgical Procedure: Performed under local anesthesia at the of the medical office. Healing is completed in a few days without scarring. The frenulum excision is painless and usually lasts only 10 minutes.

After the Procedure
Immediately after the procedure, there may be mild swelling on the upper lip or under the tongue, depending on the area treated. The patient may feel slight discomfort, which typically worsens during the first 24-48 hours and then gradually subsides. It is important for the patient to strictly follow the oral surgeon’s instructions.
If stitches are used, they are usually removed within 7 days after the procedure.

After the Procedure
Immediately after the procedure, there may be mild swelling on the upper lip or under the tongue, depending on the area treated. The patient may feel slight discomfort, which typically worsens during the first 24-48 hours and then gradually subsides. It is important for the patient to strictly follow the oral surgeon’s instructions.
If stitches are used, they are usually removed within 7 days after the procedure.

After the Procedure
Immediately after the procedure, there may be mild swelling on the upper lip or under the tongue, depending on the area treated. The patient may feel slight discomfort, which typically worsens during the first 24-48 hours and then gradually subsides. It is important for the patient to strictly follow the oral surgeon’s instructions.
If stitches are used, they are usually removed within 7 days after the procedure.