Sialadenitis

What is Sialadenitis
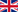
Sialadenitis is the inflammation of the salivary glands, which can be caused by bacterial or viral infections, blockage of salivary ducts, or autoimmune disorders. It primarily affects the parotid and submandibular glands, leading to pain, swelling, and difficulty eating or swallowing. This condition significantly impacts the quality of life and requires early diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications.

What is Sialadenitis
Sialadenitis is the inflammation of the salivary glands, which can be caused by bacterial or viral infections, blockage of salivary ducts, or autoimmune disorders. It primarily affects the parotid and submandibular glands, leading to pain, swelling, and difficulty eating or swallowing. This condition significantly impacts the quality of life and requires early diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications.

What is Sialadenitis
Sialadenitis is the inflammation of the salivary glands, which can be caused by bacterial or viral infections, blockage of salivary ducts, or autoimmune disorders. It primarily affects the parotid and submandibular glands, leading to pain, swelling, and difficulty eating or swallowing. This condition significantly impacts the quality of life and requires early diagnosis and treatment to prevent complications.

Causes of Sialadenitis:
- Bacterial Infections: Organisms such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus can cause inflammation when salivary flow is reduced.
- Viral Infections: Viruses such as the mumps virus and Epstein-Barr virus can also lead to sialadenitis.
- Blockage of Salivary Ducts: Conditions like sialolithiasis (salivary stones) can block the normal flow of saliva, causing swelling and increasing the risk of secondary infection.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like Sjögren’s syndrome can cause chronic inflammation of the salivary glands.
- Dehydration and Poor Oral Hygiene: Reduced salivary flow increases the likelihood of infections.

Causes of Sialadenitis:
- Bacterial Infections: Organisms such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus can cause inflammation when salivary flow is reduced.
- Viral Infections: Viruses such as the mumps virus and Epstein-Barr virus can also lead to sialadenitis.
- Blockage of Salivary Ducts: Conditions like sialolithiasis (salivary stones) can block the normal flow of saliva, causing swelling and increasing the risk of secondary infection.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like Sjögren’s syndrome can cause chronic inflammation of the salivary glands.
- Dehydration and Poor Oral Hygiene: Reduced salivary flow increases the likelihood of infections.

Causes of Sialadenitis:
- Bacterial Infections: Organisms such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus can cause inflammation when salivary flow is reduced.
- Viral Infections: Viruses such as the mumps virus and Epstein-Barr virus can also lead to sialadenitis.
- Blockage of Salivary Ducts: Conditions like sialolithiasis (salivary stones) can block the normal flow of saliva, causing swelling and increasing the risk of secondary infection.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like Sjögren’s syndrome can cause chronic inflammation of the salivary glands.
- Dehydration and Poor Oral Hygiene: Reduced salivary flow increases the likelihood of infections.

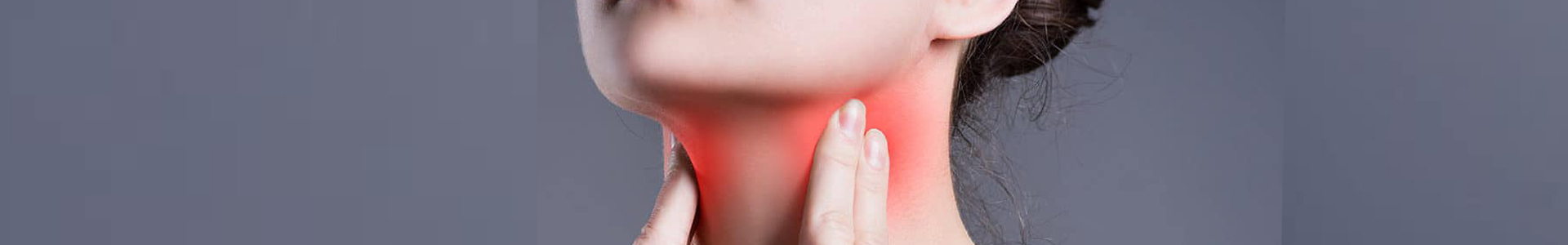
Symptoms:
- Swelling and pain in the affected glands, which worsens during eating.
- Redness and heat in the area of the swollen gland.
- Pus discharge from the mouth, fever, and chills.
- Dry mouth and difficulty swallowing.

Symptoms:
- Swelling and pain in the affected glands, which worsens during eating.
- Redness and heat in the area of the swollen gland.
- Pus discharge from the mouth, fever, and chills.
- Dry mouth and difficulty swallowing.

Symptoms:
- Swelling and pain in the affected glands, which worsens during eating.
- Redness and heat in the area of the swollen gland.
- Pus discharge from the mouth, fever, and chills.
- Dry mouth and difficulty swallowing.
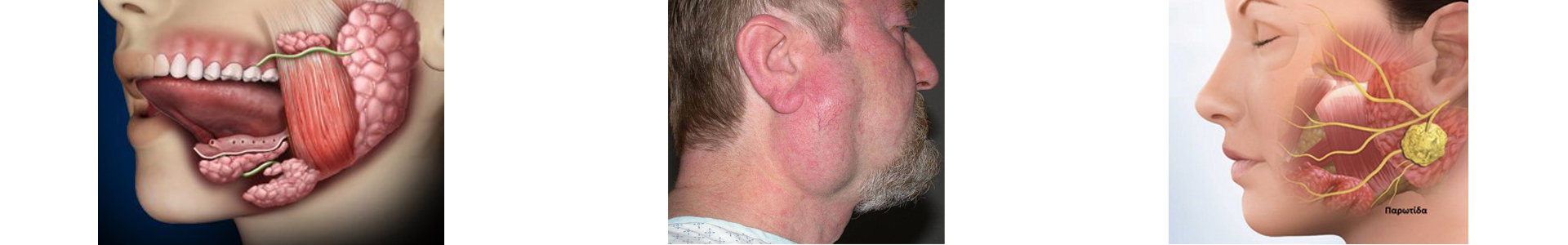

Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis involves a physical examination, imaging tests (such as ultrasound, CT scan, or sialography), and assessment of the underlying causes of the inflammation. Treatment may be either conservative or surgical:
- Conservative Treatment: Hydration, consumption of citrus fruits to stimulate salivation, warm compresses, and antibiotics for bacterial infections.
- Surgical Treatment: Removal of stones, decompression of ducts, or even removal of the affected gland in severe cases.

Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis involves a physical examination, imaging tests (such as ultrasound, CT scan, or sialography), and assessment of the underlying causes of the inflammation. Treatment may be either conservative or surgical:
- Conservative Treatment: Hydration, consumption of citrus fruits to stimulate salivation, warm compresses, and antibiotics for bacterial infections.
- Surgical Treatment: Removal of stones, decompression of ducts, or even removal of the affected gland in severe cases.

Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis involves a physical examination, imaging tests (such as ultrasound, CT scan, or sialography), and assessment of the underlying causes of the inflammation. Treatment may be either conservative or surgical:
- Conservative Treatment: Hydration, consumption of citrus fruits to stimulate salivation, warm compresses, and antibiotics for bacterial infections.
- Surgical Treatment: Removal of stones, decompression of ducts, or even removal of the affected gland in severe cases.

Prevention:
Prevention focuses on maintaining good oral hygiene, drinking plenty of water to keep saliva production steady, avoiding smoking and alcohol, and chewing sugar-free gum or candies to stimulate salivation.
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications such as abscess formation or chronic inflammation. For effective management of sialadenitis, it is crucial to consult a specialist

Prevention:
Prevention focuses on maintaining good oral hygiene, drinking plenty of water to keep saliva production steady, avoiding smoking and alcohol, and chewing sugar-free gum or candies to stimulate salivation.
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications such as abscess formation or chronic inflammation. For effective management of sialadenitis, it is crucial to consult a specialist

Prevention:
Prevention focuses on maintaining good oral hygiene, drinking plenty of water to keep saliva production steady, avoiding smoking and alcohol, and chewing sugar-free gum or candies to stimulate salivation.
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications such as abscess formation or chronic inflammation. For effective management of sialadenitis, it is crucial to consult a specialist